Slitting
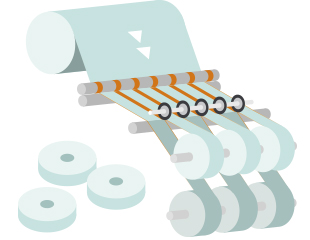
The slitter is a machine that winds out rolled sheets of paper, nonwoven fabric, film, adhesive tape, metallic foil and other sheets while cutting them with blades in the direction of flow, and then winding back the slit materials as individual rolls.
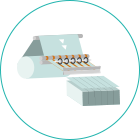
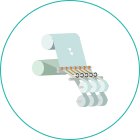
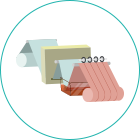
The figure illustrates the general structure of the slitter.
The original fabric (material) set in the reeling-off section is fed and cut by slitting blades as it passes through the pass line (roll).
It passes through the pass line (roll) once again while being wound into rolls in the winding section (products).
-
General Structure of the Slitter
In many cases, raw rolls are generally wrapped around a “paper tube” made of paper or a “plastic core” made of ABS, PE resin, etc. as a support. It can be set in the unwinding part by passing the "shaft" through the tube or plastic core.
Rolls on the pass line are generally metal rolls plated with hard chrome or rubber as the main material.
In addition, there are many cases where "expander rollers" that are intentionally curved for the purpose of eliminating wrinkles are installed on the pass line.
In addition, special rollers such as silicon rollers may be installed depending on the characteristics of the material to be cut. -
Optimum Cutting According to the Materials
The slit blade used for cutting is a pair of upper and lower blades, and it is common to cut by passing the material between the upper and lower blades. called a "blade". By using different blade angles and materials according to the characteristics of the material to be cut, it is possible to further improve the quality of the product.
In addition, depending on the material to be cut, the "share blade (round blade)" may not reach the target quality. Sometimes a "gang blade" is used which is suitable for slitting foil.
"Gang blades" are blades that are rarely installed in factories due to versatility and management issues. -
Winding Section
Like the unwinding section, the winding section has a support for winding up the product. It is common to use a "paper tube" made of paper or a "plastic core" made of ABS, PE resin, etc. There are two types of rewinding shafts, one and two. Ordinary paper is wound with one shaft, but films and adhesive tapes are often wound with two shafts. For those with a single winding shaft, there is a type that winds up on the shaft only (center drive) and a type that winds up while holding down one winding shaft with one upper and two lower rollers (three in total) (surface formula).
| Type of paper | Micro slitters | Micro slitters 26 |
|---|---|---|
| Wide and large slitters | ||
| Small roll (coreless) | ||
| Single axis slitters | ||
| Double axis slitters | ||
| Type of film | Micro slitters | |
| Traverse processing | Traverse processing 94 | |
| Double axis slitters | Double axis slitters 98 | |
| Sheet slitter | Sheet slitter 103 | |
| Other | For metallic foil and RFID | Slitting/For metallic foil and RFID |
| For batteries | Slitting/For batteries | |
| Adhesive products | Slitting/Adhesive products |